Story at a glance:
- The long-term, fade-resistant performance of Kynar 500 solvent-based finishes have been trusted for decades.
- In 2025 the Kynar 500 brand is celebrating its 60th anniversary. Today Kynar Aquatec provides similar performance in a water-based resin formulated for field applications.
- Coatings formulated with Kynar Aquatec PVDF resin can be applied easily in the field to a variety of surfaces, including metals, plastics, wood, concrete, stucco, EIFS and previously painted surfaces.
More than half a century ago Kynar 500® polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) resins were introduced by Arkema for factory-applied OEM coating systems used on exterior building materials like aluminum doors, window frames, facades, and roofing panels. The resin technology, dispersed in solvents, requires baking at 400 to 500 degrees Fahrenheit to react and cure, making it only for metal surfaces that can withstand these high temperatures. While the technology has unprecedented weathering performance and is well-established in the global architectural industry, its high baking temperatures limit its use in field-applied settings.
Fast-forward a few decades and the architectural industry’s demand for a PVDF-based coating system that can be field-applied, air-dried, and used on multiple substrates—coupled with environmental regulations and health and safety concerns associated with high VOC emissions—prompted Arkema to create a water-based version of the resin. Kynar Aquatec® resin now has nearly 25 years of identical performance to Kynar 500 finishes in harsh outdoor environments. Coatings formulated with Kynar Aquatec PVDF resin can be applied easily in the field to a variety of surfaces, including metals, plastics, wood, concrete, stucco, EIFS, and previously painted surfaces.
PVDF Provides Long-Term Performance
Kynar Aquatec is a tough, engineered thermoplastic polymer with super-strong carbon-fluorine bonds that do not break down under exposure to the elements. Since 2009 Kynar Aquatec resin has been a key ingredient in APV Engineered Coatings’ field-applied NeverFade® Exterior Paints.
Along with complex inorganic pigments, Kynar Aquatec resin gives the paints excellent weatherability, color retention, abrasion resistance, and minimal film erosion, allowing them to outlast high-performance urethane and acrylic latex-based paints, even when exposed to extreme UV rays, high temperatures, humidity, and abrasion. The paints also hinder mold, mildew, and dirt pickup better than traditional high-performance paints, which break down under UV exposure, eroding, and chalking over time and eventually leaving the building’s substrate bare and open to damage from the elements.
The figure below shows the extent to which UV energy breaks down common coating binders, reducing their mechanical protection properties. Note that PVDF resin has very minimal absorption of UV energy, allowing it to resist photochemical degradation and maintain original film thickness, making it ideal for field applications needing strong UV resistance.
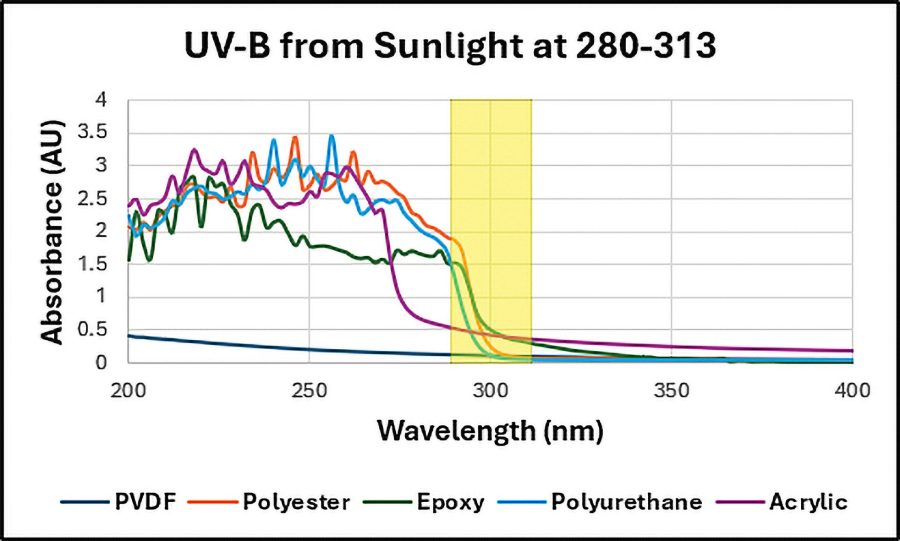
Image courtesy of APV Engineered Coatings
Chalking and coating film erosion negatively impacts surface energy. The lower surface energy of NeverFade paints enables these surfaces to inherently resist mold growth yet be recoated to touch up any physical damage. Because these coatings show no fading, the repaired area will match the surrounding areas.
In the case of NeverFade the Kynar Aquatec PVDF resin greatly contributes to the paint formula’s low surface energy properties in a cured state. One of the challenges from a chemistry standpoint is properly formulating the paint to completely wet out the surface. Proper wetting provides continuous coverage of the paint film, adhesion, and optimum aesthetics as it is applied, and this must be accomplished through proprietary performance additives. As NeverFade dries and cures, the resultant coating yields a much lower surface energy with a higher contact angle and non-stick properties.
The images below show contact angles of paints with various resin binders. In this laboratory test a bead of water is dropped onto a coated surface, and the angle between the bead of water and the paint film is measured with a goniometer. The greater the angle, the better the paint’s ability to resist penetration by water, dirt, and debris, and the easier it will be to clean.
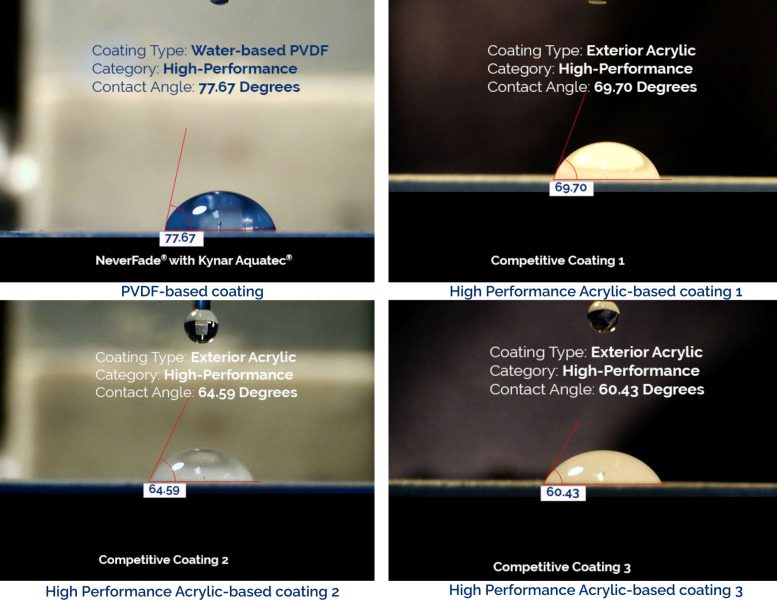
Image courtesy of APV Engineered Coatings
To translate this lab testing into real-life performance, the figure below demonstrates the ability of a paint made with Kynar Aquatec resin to resist film erosion after outdoor exposure compared with a high-performance acrylic resin-based paint. Both formulations shown utilize cobalt blue pigment, which is one of the most lightfast of the blue pigments. Therefore, any degradation of the paint from weathering is related to the resin binder system only.
After seven years of exposure in south Florida at 45° angle facing south, the acrylic resin-based paint demonstrates film erosion and significant fading, chalking, and degradation. The Kynar Aquatec based paint is still intact with no film erosion and, therefore, negligible fading and chalking, thus protecting the substrate for a much longer period. This is especially advantageous in southern coastal environments where the harsh sunlight coupled with salt can speed the degradation of building products.

Image courtesy of APV Engineered Coatings
Sustainability Advantages of Field-Applied Kynar Aquatec–Based Paints
Sustainability benefits of using field-applied NeverFade Exterior Paints with Kynar Aquatec include:
- Longer lifespans of painted surfaces for less material consumption and landfill-bound waste.
- Protection of the substrate for increased life cycle of the structure.
- Reduced heat buildup and related energy consumption, thanks to high total solar reflectance, as well as dirt shedding and mold/mildew resistance properties that keep building surfaces cleaner and further improve their solar reflectance.
- Reduced consumption of paint, packaging, and related resources because the paints can be applied at a much lower thickness than acrylic-based paints, which need significantly higher thicknesses to offset film erosion over time.
- Ultra-low concentrations of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)—less than 50 grams/liter—for fewer nuisance odors that can be objectionable and disruptive to building occupants. The paints meet SCAQMD Rule 1113 and 40 CFR Part 59, Subpart D, national VOC Emission Standards for Architectural Coatings.
Benefits for Specifiers and Building Owners
With Kynar Aquatec PVDF-based paints, architects and project specifiers are better able to design and specify bright and bold colors, secure in the knowledge that those colors will remain true for the long term.
On the other end of the spectrum, high-performance, PVDF-based paints are critical for white exterior surfaces as well, especially in high humidity environments. When acrylic latex and urethane paints break down and the film turns chalky, it is not always noticeable against the white surface, but the paint is losing its protective qualities due to film erosion. The same properties that allow the PVDF-based paints to resist color fading also allow them to resist the dirt, bugs, mold, and mildew that can turn a vibrant building exterior into a maintenance-intensive eyesore.
The trusted long-term performance of Kynar Aquatec is one of the reasons APV can offer a 15-year product-and-labor guarantee for NeverFade, which states that the paint will not fade by a Delta E of five or higher. Transferable to future building owners, the guarantee is unique to the architectural paint and coatings industry.


